In today’s dynamic market, businesses face inherent unpredictability, from sudden shifts in consumer preferences to global supply chain disruptions. The ability to anticipate future demand is no longer a luxury but a strategic imperative for survival and growth. Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for products or services over a specific period. It involves analyzing historical data, current market conditions, and various influencing factors to make informed predictions about future demand patterns. This proactive approach allows companies to optimize operations, minimize costs, and effectively meet customer needs.
Once considered a complex analytical exercise primarily for large corporations, accurate demand forecasting has become a non-negotiable for businesses of all sizes, particularly within the supply chain and retail industries. It represents a fundamental shift from reactive firefighting to proactive strategy, serving as the cornerstone of data-driven decision-making. This report will delve into the critical benefits of robust demand forecasting, shed light on the significant risks of neglecting it, and provide a clear, simplified path to its implementation for sustainable growth and profitability.
- The Hidden Costs of Guesswork: Why Ignoring Demand Forecasting is a Risky Business
- The Power of Prediction: Unlocking Core Benefits with Accurate Demand Forecasting
- Real-World Success: How Leading Businesses Leverage Demand Forecasting
- Getting Started: A Simplified Path to Implementing Demand Forecasting
- Conclusion: Embrace Foresight, Drive Prosperity
The Hidden Costs of Guesswork: Why Ignoring Demand Forecasting is a Risky Business
Without reliable demand forecasts, businesses risk operational inefficiencies, significant financial losses, and reduced customer satisfaction. Ineffective demand planning has far-reaching repercussions, affecting every part of the business chain down to the customer.
Stockouts and Lost Sales
Underestimating demand leads directly to stockouts, a critical situation where products are unavailable precisely when customers wish to purchase them. This results in immediate lost sales opportunities and deeply frustrates customers. When customer demand exceeds available stock levels, sales opportunities are lost, and customer dissatisfaction becomes inevitable. The impact extends beyond the immediate transaction; a single stockout experience can severely damage a brand’s reputation, erode customer trust, and prompt consumers to seek alternatives from competitors. Many shoppers, faced with an unavailable product, will simply contact a competitor rather than wait for a store to restock. This immediate behavioral shift can lead to long-term customer churn and a reduction in market share. The progression from an initial stockout to a loss of brand equity illustrates how a seemingly simple operational failure can have profound, lasting impacts on a company’s intangible assets like reputation and customer loyalty.
Excess Inventory and Capital Drain
Conversely, overestimating demand leads to excess inventory, which ties up valuable capital in unsold goods and unnecessarily blocks warehouse space. This capital, which could otherwise be deployed for other critical business needs, becomes stagnant. The consequences include increased storage costs, higher risks of product obsolescence or spoilage (a particularly acute problem in industries like food where products can spoil quickly if demand is too low), and the eventual need for costly discounts or bundling strategies to move stagnant stock. When capital gets stuck in excess inventory, and warehouse spaces are blocked, carrying costs increase, along with the risks of damage to inventory. This situation highlights the significant opportunity cost of tied-up capital. The financial burden isn’t merely the direct cost of storage; it’s the foregone potential of that capital, which could have been invested in research and development, marketing campaigns, market expansion, or other strategic initiatives. This reduction in liquidity and financial flexibility can hinder a business’s ability to grow and innovate compared to more agile competitors.
Operational Inefficiencies and Increased Costs
Inaccurate forecasts disrupt production schedules, leading to either under-utilization or over-utilization of critical resources such as labor and machinery. This directly results in increased production costs, reduced productivity, and potentially idle or over-active machinery. Furthermore, companies frequently incur premium charges for expedited shipments to meet unexpected demand, which significantly eats into profit margins. Without proper planning, the entire supply chain becomes less efficient, creating a ripple effect of increased expenses and reduced output. This points to a systemic supply chain fragility. The constant need for reactive, last-minute operational adjustments leads to heightened costs, diminished efficiency, and increased stress on supply chain partners. This creates a fragile and less resilient supply chain, highly vulnerable to future disruptions, perpetuating a cycle of inefficiency rather than fostering robust, predictable operations.
Eroding Customer Loyalty
Modern customers expect instant gratification and seamless omnichannel experiences. Ineffective demand planning directly leads to delays in meeting customer orders, incorrect product deliveries, and a general inability to consistently meet customer expectations. This directly impacts customer satisfaction, leading to a loss of trust and a higher likelihood of customers switching to competitors who can fulfill their needs promptly. If a business cannot fulfill orders within agreed timelines, customers may become disappointed and move to a competitor. This can quickly lead to customer dissatisfaction levels hitting rock bottom, with customers queuing up to competitors. This situation reveals the hidden cost of customer acquisition. Reduced customer satisfaction and increased customer churn necessitate higher spending on new customer acquisition efforts. Acquiring new customers is typically more expensive than retaining existing ones, thereby imposing a long-term financial burden on the business that stems directly from neglecting customer experience.
The Ripple Effect of Poor Demand Forecasting

This infographic visually encapsulates the cascading negative effects discussed in this section. By presenting quantifiable impacts, such as up to 65% lost sales, alongside qualitative consequences like eroding customer loyalty, it provides a compelling, easy-to-digest summary of the risks. The visual flow reinforces the idea that these problems are interconnected and stem from a single root cause, making the argument for demand forecasting more urgent and clear.
The Power of Prediction: Unlocking Core Benefits with Accurate Demand Forecasting
Accurate demand forecasting provides valuable insights that drive critical business decisions, helping companies optimize operations, improve cash flow, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to more sustainable operations. It is a strategic capability that enables smarter decision-making, leaner operations, and improved profitability.
Optimized Inventory Management
Accurate forecasts enable businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, striking a crucial balance between having enough products to meet demand and avoiding costly overstocking. This balance is particularly vital for businesses with limited storage space or those dealing with perishable goods, where overstocking can quickly lead to waste and financial loss. The direct impact includes reduced holding costs, prevention of dead stock, and ensuring that fast-moving items are consistently available to customers. Businesses that implement advanced forecasting strategies often report significant reductions in excess inventory, with some achieving 15-25% reductions. This optimization leads to greater capital efficiency and agility. By reducing the capital tied up in stock, businesses gain increased working capital and financial flexibility. This enhanced liquidity enables them to invest in growth opportunities, respond swiftly to market shifts, and maintain financial stability, fostering greater overall business agility.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Demand forecasting streamlines production and supply chain operations, allowing manufacturers to schedule production more efficiently, reduce idle time, and lower overall production costs. This process helps align production with actual market needs, leading to smarter resource utilization and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process. The result is improved allocation of resources, including personnel and equipment, and optimized supply chains capable of delivering products wherever and whenever they are needed. Such improvements can lead to significantly quicker turnaround times, with some operations seeing a 1.5x increase in speed. This progression from efficiency to sustainability is notable. Optimized production and reduced waste directly lead to lower resource consumption and less discarded material. This contributes positively to environmental goals and fosters a more sustainable operation, which can further improve brand image, appeal to eco-conscious consumers, and potentially offer long-term regulatory compliance advantages.
Boosting Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Meeting consumer demands quickly and consistently significantly improves a company’s reputation and customer satisfaction. Accurate forecasts ensure that products are available precisely when needed, preventing delays and creating a seamless buying experience for customers. This reliability builds trust, leading to higher satisfaction levels, increased repeat purchases, and stronger brand loyalty over time. When customers consistently find the right product in stock, trust builds, and that reliability leads to higher satisfaction and repeat purchases. This establishes a customer-centric growth engine. Consistent product availability and a positive customer experience directly increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. This, in turn, boosts customer lifetime value (CLV) and generates organic word-of-mouth marketing. The outcome is a reduced need for new customer acquisition efforts and a self-reinforcing growth engine driven by customer advocacy, positioning customer satisfaction not merely as a goal but as a powerful driver of sustainable revenue.
Strategic Decision-Making and Competitive Edge
Long-term demand forecasting provides invaluable insights into future market trends and evolving customer preferences, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about product development, market expansion, and overall business strategy. It transforms raw data into actionable intelligence, allowing businesses to proactively steer their operations rather than merely reacting to market shifts. Businesses can effectively tailor marketing efforts, plan promotions around expected demand, and respond faster to changing market conditions. This proactive approach provides a significant competitive advantage, allowing businesses to outperform competitors who lack this capability. This capability fosters proactive market leadership. Data-driven strategic planning enables the early identification of market trends and shifts in consumer behavior. This allows businesses to innovate, launch new products, or enter new markets ahead of competitors, leading to the establishment of market leadership, increased market share, and sustained competitive advantage. It represents a shift from reactive business strategy to one of strategic foresight.
Significant Cost Savings and Improved Profitability
By maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing waste, and streamlining operations, businesses can achieve substantial cost savings across various functions. This directly translates to improved profit margins and a stronger bottom line. For instance, demand forecasting helps businesses save money by making inventory and resource management more efficient, with the potential to cut material waste by up to 60% and lower operational costs by 22%. Companies that implement these practices can expect quantifiable impacts, including 20-30% reductions in overall inventory investment and 3-5 percentage point improvements in gross margins. This leads to enhanced investor confidence and valuation. Improved profitability and operational efficiency result in stronger financial performance and more predictable cash flow. This, in turn, increases investor confidence and can lead to a higher company valuation, facilitating easier access to capital for expansion, acquisitions, or weathering economic downturns, thereby securing long-term financial health.
Real-World Success: How Leading Businesses Leverage Demand Forecasting
The theoretical benefits of demand forecasting are powerfully demonstrated by real-world applications in leading global companies. Their success stories underscore the tangible return on investment and strategic advantages gained.
Global Giants Leading the Way
- Amazon: The online retail giant utilizes demand forecasting extensively, employing machine learning models and other analytical tools to analyze product demand in real-time. This sophisticated approach allows Amazon to fulfill orders efficiently and optimize inventory, ensuring that sufficient goods are always in stock to meet customer inquiries quickly and effectively.
- Walmart: As one of the world’s largest retailers, Walmart optimizes its inventory management across more than 1,100 stores in 27 countries by leveraging demand forecasts. They employ analytical tools and technologies to effectively manage order volumes and inventory levels, with the overarching aim of optimizing their supply chain, preventing bottlenecks, increasing sales, and enhancing overall profitability.
- Coca-Cola: Coca-Cola employs demand forecasting to analyze demand across various regions and markets. This enables the company to plan the production of its beverages more effectively, make informed decisions regarding adjusting production capacities, and optimize production and delivery costs through intelligent transport and storage strategies.
Quantifiable Impact: A Case Study in Rapid ROI
A compelling example of the tangible benefits of demand forecasting comes from a cleaning products and services company. With annual revenues of $70 million, over 2,000 product references, and 5,000 customers, this company achieved remarkable results by implementing advanced demand forecasting.
The specific improvements and rapid return on investment included:
- Service Level: An increase of 10 points, reaching an impressive 99.1%.
- Decrease in Lack of Stock: A reduction of 9 points, now standing at a mere 0.9%.
- Logistics Costs: A decrease of 2.25%, translating to approximately $5,000 USD in monthly savings.
- Supplier Anticipation: The ability to anticipate suppliers with three months’ notice, which significantly aids in fulfilling deliveries.
- New Strategic Customers: The successful closure of two new strategic customers, directly attributed to the use of the demand forecasting platform.
- Decreased Inventory Levels: A substantial reduction in excess stock by over $450,000.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Achieved in an exceptionally short timeframe of just three weeks.
These results illustrate the “small wins” compounding effect. The rapid, three-week ROI demonstrates that significant, measurable benefits can be achieved very quickly, even for mid-sized businesses. This speed of return encourages faster adoption and continuous investment in forecasting technologies. It creates a positive feedback loop where initial successes build momentum for deeper integration and optimization across the organization, leading to compounding benefits over time and countering the perception that forecasting is a long, drawn-out process with delayed returns.
Broader industry statistics further support these findings: the ability to accurately forecast demand through predictive analysis allows the retail sector to reduce errors from 20% to 50%. Subsequently, lost sales can be reduced by up to 65%. Companies that improve their forecasting accuracy are also 10% more likely to increase sales and income yearly.
Tangible Returns: The Business Impact of Demand Forecasting
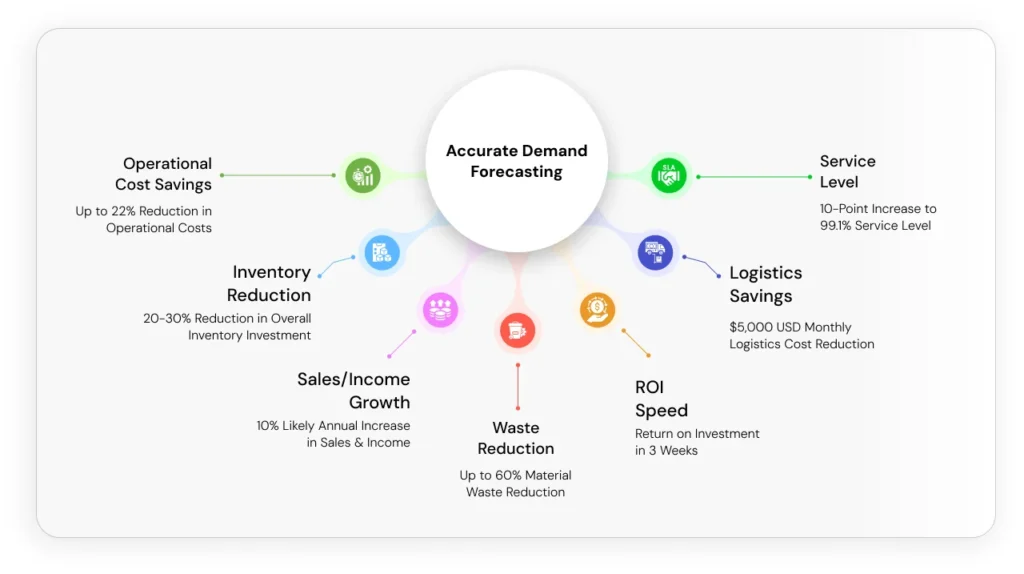
This infographic provides a powerful, at-a-glance summary of the positive, quantifiable outcomes of effective demand forecasting. By combining general industry statistics with specific case study numbers, it provides concrete evidence of return on investment, making a strong business case. The visual format ensures these impressive figures are immediately digestible and memorable for decision-makers.
Getting Started: A Simplified Path to Implementing Demand Forecasting
Implementing demand forecasting does not have to be an overwhelming task. A structured approach, starting with clear objectives and leveraging available data, can set any business on the path to greater foresight and profitability.
Key Steps in the Demand Forecasting Journey
1. Define Your Goals and Scope
Before any other steps, it is crucial to clarify the precise purpose of the forecast. Will it be primarily used for financial planning, inventory management, sales planning, or a combination of these?. The defined goals will guide subsequent decisions regarding the time horizon of the forecast, the level of granularity required, and the desired output format. Being clear about goals provides guidance on many subsequent decisions; without this clarity, the rest of a forecasting process’s design is merely guesswork. This step establishes strategic alignment as a foundational element. Clearly defined goals ensure that the entire forecasting effort is aligned with broader business objectives. This prevents “analysis paralysis” and ensures that resources are focused on generating truly actionable insights rather than simply collecting data. Ultimately, this maximizes the strategic value and adoption of the forecast across different departments, fostering a unified business strategy.
2. Gather and Prepare Relevant Data
Collect all available historical data, with sales records being the primary source. Even a few months’ worth of data can prove valuable for initial forecasting efforts. Beyond internal sales data, it is important to consider a wide array of external factors. These include general economic conditions, prevailing market trends, predictable seasonal patterns, and any special events that might influence demand. Factors such as weather patterns or demographic shifts can also play a significant role depending on the industry. The historical evolution of sales for each product, the time of year (e.g., Christmas, Black Friday), consumer behavior, and regulatory regulations in the sector are all important considerations. This step highlights the power of data synergy. Combining internal historical sales data with external market indicators creates a more holistic and robust dataset. This enables the identification of complex, non-obvious patterns and causal relationships that might otherwise be missed. The result is significantly more accurate and resilient forecasts that can anticipate external shocks and capitalize on emerging trends, moving beyond mere extrapolation of past performance.
3. Select Appropriate Forecasting Methods
The choice of forecasting methods should be suitable for the business’s specific needs, taking into account data availability, the desired planning horizon, and the required level of accuracy.
- Quantitative Forecasting: This approach relies on objective metrics derived from historical data and statistical analyses. Common methods include time series analysis, regression, moving averages, and exponential smoothing. Quantitative methods are generally the most accurate when sufficient historical data is available.
- Qualitative Forecasting: This method is based on subjective metrics such as expert opinions, market research, and customer surveys. It is typically employed when historical data is limited, for example, during new product launches or in highly volatile markets.
- Advanced Methods (AI/ML): Machine learning models possess the capability to process large volumes of data and detect complex patterns that might be invisible to traditional methods. These advanced tools often outperform legacy models in terms of accuracy and agility.
At its best, demand forecasting combines both qualitative and quantitative approaches. The availability of advanced AI/ML tools increasingly emphasizes the human-AI collaboration imperative. While AI/ML tools provide increased accuracy and speed in forecast generation, the human role shifts from manual calculation to strategic interpretation and validation. This fosters a collaborative environment where human market understanding and insights can validate and refine AI-generated forecasts, leading to more robust and trusted predictions than either could achieve independently.
4. Implement the Chosen Method and Generate Forecast
Once the data is prepared and the appropriate method(s) selected, the next step involves systematically applying the chosen methodology to the data to generate initial forecasted values. This process yields preliminary insights into future demand patterns and potential fluctuations.
5. Evaluate, Refine, and Correct
After generating the initial forecast, it is essential to assess its accuracy and reliability by comparing the forecasted values to actual demand data. This evaluation helps identify any discrepancies and understand the effectiveness of the chosen forecasting method. Errors or biases that may arise from data inaccuracies, modeling assumptions, or unforeseen external factors must be identified and rectified. Continuous validation is a key element of this process, ensuring the forecast remains relevant and reliable. The initial forecast results are evaluated to assess their accuracy and reliability, with a comparison made between forecasted values and actual demand data to identify discrepancies. This step underscores the importance of iterative improvement and adaptability. Continuous evaluation and refinement lead to the identification and correction of forecast errors and biases, which in turn contributes to the development of a more accurate and adaptable forecasting model over time. This process ultimately increases organizational resilience to market volatility and unexpected disruptions, allowing for agile strategic adjustments.
6. Integrate and Monitor
The final, refined forecast must be integrated into the business’s overall planning processes. This includes informing budgeting, production planning, inventory management, and resource allocation. The forecast acts as a valuable input for these critical functions. Furthermore, the forecast needs to be regularly monitored and updated to reflect any changes in market conditions, customer preferences, or other influencing factors that may emerge over time. Once integrated into the business planning process, the forecast needs to be regularly monitored and updated as necessary. This integration fosters enterprise-wide synergy and a data-driven culture. Integrating forecasts across various departments improves cross-functional communication and alignment, leading to the creation of a unified, data-driven organizational culture. This enhances overall business performance, as all departments operate from a common understanding of future demand, leading to synergistic improvements and more cohesive strategic execution.
Your 6-Step Demand Forecasting Journey
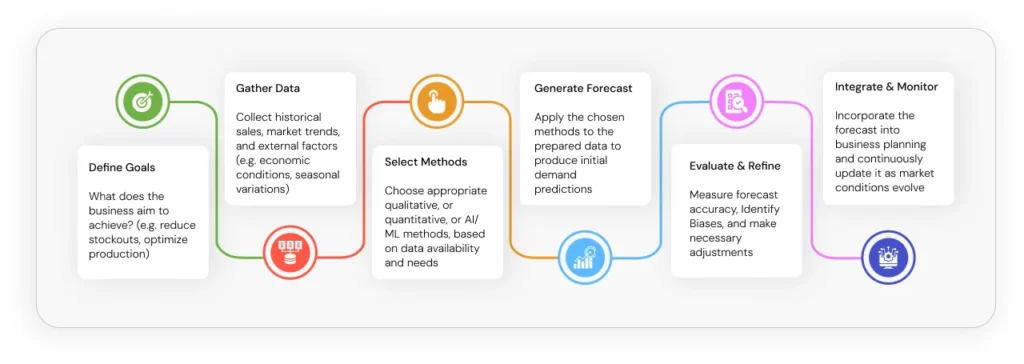
- Define Goals: What does the business aim to achieve? (e.g., reduce stockouts, optimize production)
- Gather Data: Collect historical sales, market trends, and external factors (e.g., economic conditions, seasonal variations)
- Select Methods: Choose appropriate qualitative, quantitative, or AI/ML methods based on data availability and needs
- Generate Forecast: Apply the chosen method(s) to the prepared data to produce initial demand predictions
- Evaluate & Refine: Measure forecast accuracy, identify biases, and make necessary adjustments
This infographic provides a clear, actionable roadmap for businesses looking to implement or improve demand forecasting. Its step-by-step nature breaks down a complex process into manageable stages, making it less intimidating for readers. The visual flow ensures easy comprehension and serves as a practical guide, reinforcing the actionable nature of the blog post.
Conclusion: Embrace Foresight, Drive Prosperity
Demand forecasting is more than just predicting numbers; it is about building resilience, optimizing resources, delighting customers, and securing a competitive edge in an unpredictable world. It serves as the fundamental input for a company’s operations, directly impacting service levels and the ability to meet demand. Businesses that embrace foresight through accurate demand forecasting are not merely surviving; they are thriving. They move beyond simply reacting to market shifts to proactively shaping their future, ensuring sustainable growth and long-term prosperity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ready to take control of your demand and inventory?
Contact us to build a smarter, forecast-driven strategy.




