- The Retail Data Explosion and Its Challenges
- Common Pain Points in Retail Data Management
- The Limitations of Traditional Data Architectures in Retail
- What is a Lakehouse Architecture?
- Why Retail Needs Lakehouse Architecture?
- How Lakehouse Solves Retail Challenges?
- Benefits of Lakehouse for Retail Businesses
- Implementation Roadmap
- Conclusion: The Future of Retail Data is Unified
The Retail Data Explosion and Its Challenges
In today’s hyper-competitive retail landscape, data is the new currency. However, many retailers are drowning in data but starving for insights. Fragmented data silos, legacy systems, and complex architectures prevent businesses from unlocking the true potential of their data, leading to missed opportunities, inefficient operations, and ultimately, lost revenue.
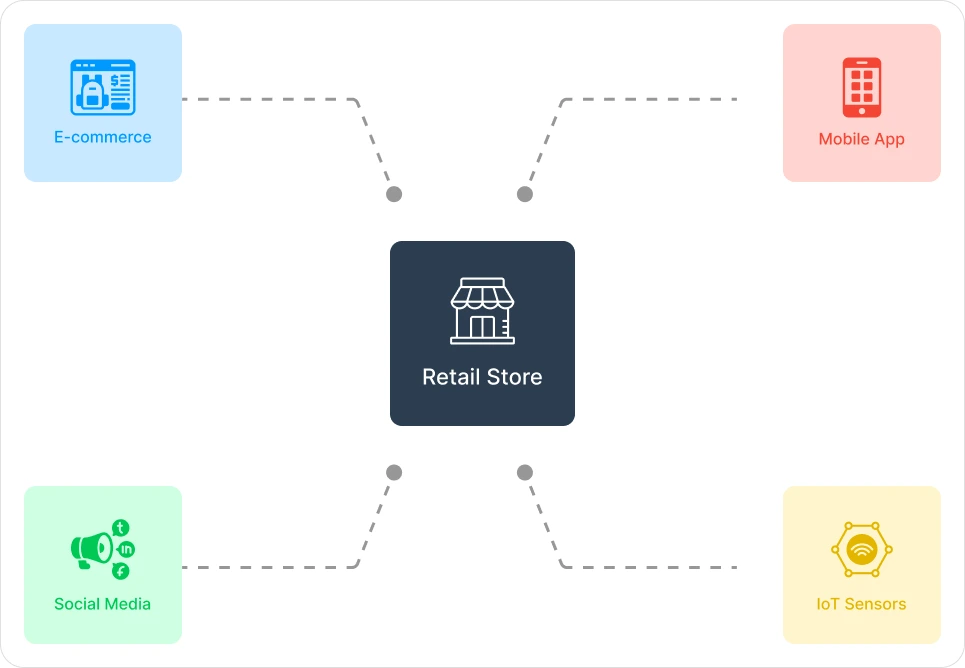
The Modern Retail Data Challenge
- Explosion of data sources (in-store, online, mobile, social)
- Real-time inventory management struggles
- Customer 360° view complexity
- Siloed systems causing delayed decisions
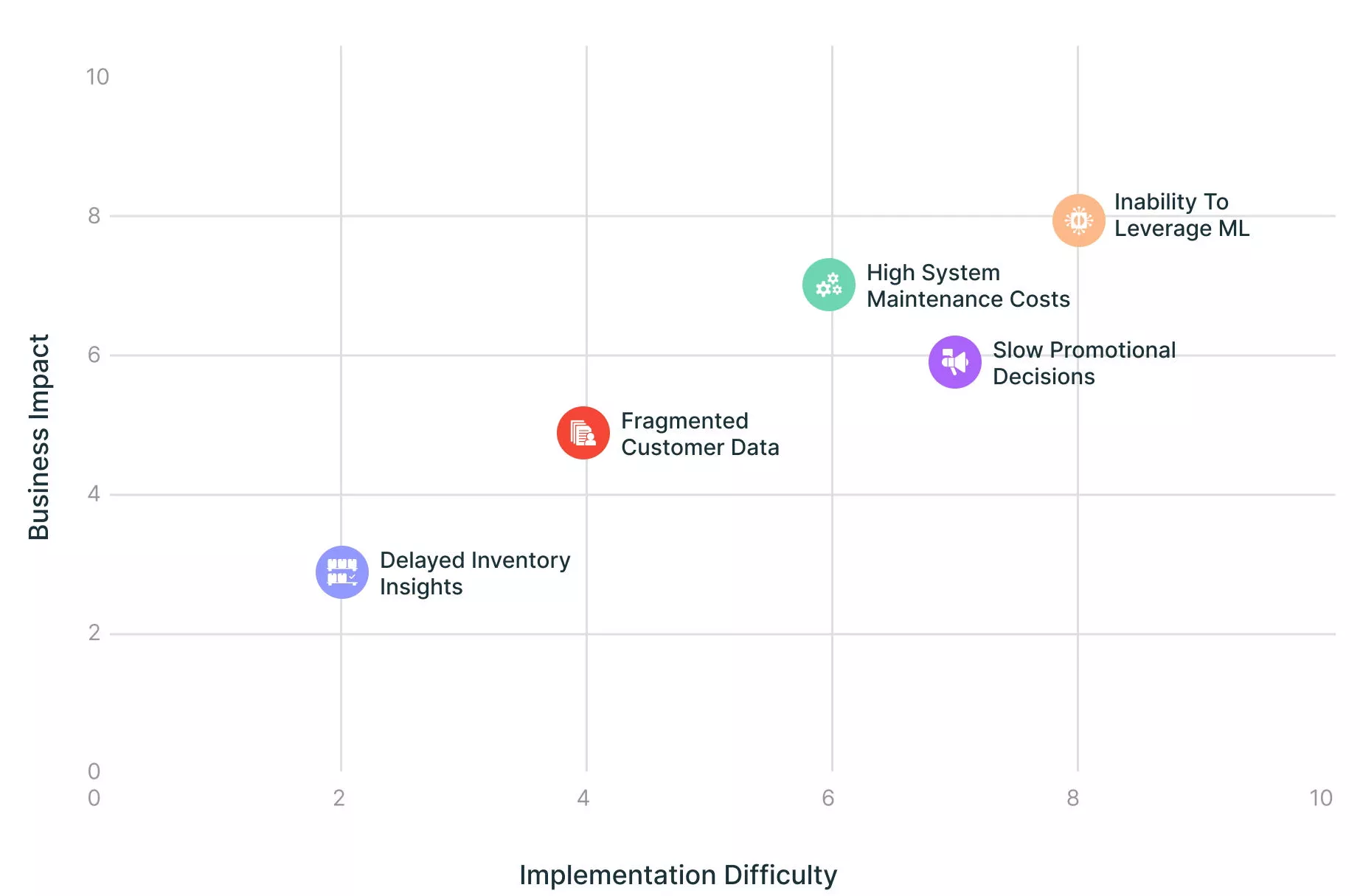
Common Pain Points in Retail Data Management
Delayed inventory insights
Retailers often lack real-time visibility into inventory levels across stores, warehouses, and channels. This delay can result in stockouts or overstock situations, directly impacting sales and customer satisfaction.
Fragmented Customer Data
Customer information is frequently siloed in disparate systems—such as point-of-sale, e-commerce, loyalty programs, and marketing platforms. This fragmentation makes it difficult to create a unified customer profile, hindering effective personalization and omnichannel engagement
High maintenance Costs
Legacy architectures force retailers to operate and maintain separate data warehouses, lakes, and operational databases. This duplication increases infrastructure and licensing costs, as well as the burden on IT teams
Slow Time-to-Insights
Complex data pipelines and slow batch processing mean that insights for pricing, promotions, and merchandising are often outdated by the time they reach decision-makers. This lag reduces agility in responding to market trends and customer preferences
Inability to leverage Machine Learning
Without a unified, high-quality data foundation, deploying advanced analytics and machine learning models is challenging. This limits the retailer’s ability to deliver personalized recommendations, targeted marketing, and dynamic pricing at scale
The Limitations of Traditional Data Architectures in Retail
Traditional data warehouses, while effective for structured data, struggle to handle the volume, velocity, and variety of data generated by modern retail operations. Data lakes, on the other hand, often become data swamps without proper governance and data quality measures, making it difficult to extract meaningful insights.

What is a Lakehouse Architecture?
A lakehouse architecture is a modern data platform that combines the best features of traditional data warehouses and data lakes. It supports the reliable management of structured and unstructured data, offering the performance, governance, and ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions of a data warehouse, while maintaining the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of a data lake. This unified approach enables retailers to ingest, store, process, and analyze massive volumes of diverse data—from point-of-sale transactions to online customer interactions—in a single system.
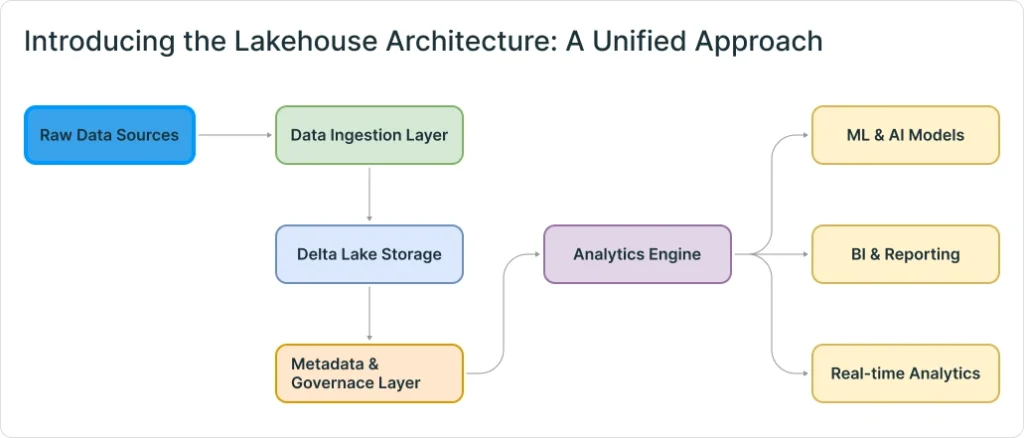
The Lakehouse architecture offers a game-changing solution by combining the best of both worlds. It provides the data management capabilities and ACID transactions of a data warehouse with the scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of a data lake.
Why Retail Needs Lakehouse Architecture?
Retailers today face an explosion of data from multiple sources: in-store sensors, e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, social media, and supply chain systems. Traditional architectures struggle with:
- Data Silos: Data scattered across multiple systems, making unified analytics difficult.
- Slow Insights: Legacy systems delay time-to-insight, impacting real-time decision-making.
- High Costs: Maintaining separate warehouses, lakes, and operational databases increases cost and complexity.
- Limited Personalization: Fragmented data hinders the deployment of advanced analytics and machine learning for personalization.
A lakehouse architecture addresses these pain points by providing a single source of truth, enabling real-time analytics, supporting advanced AI/ML workloads, and lowering infrastructure costs.
How Lakehouse Solves Retail Challenges?
Lakehouse architecture addresses these retail pain points by:
- Unifying data storage: All data—structured, semi-structured, unstructured—resides in a single platform.
- Supporting ACID transactions: Ensures data consistency and reliability for analytics and reporting.
- Enabling real-time analytics: Supports fast, up-to-date decision-making across inventory, pricing, and customer engagement.
- Simplifying machine learning: Data scientists can access high-quality, governed data for personalization and predictive analytics.
- Reducing costs: Fewer systems to maintain, with cloud-native scalability and lower storage costs compared to warehouses.

Benefits of Lakehouse for Retail Businesses
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unified Data Platform | Breaks down silos—single source for all retail data |
| Real-Time Insights | Enables instant analytics for inventory, sales, and customer behavior |
| Advanced Analytics & ML | Facilitates AI-driven personalization, demand forecasting, and more |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces infrastructure and operational costs |
| Data Governance & Security | Ensures compliance and data quality across all data types |
| Flexibility & Scalability | Easily adapts to new data sources and business needs |
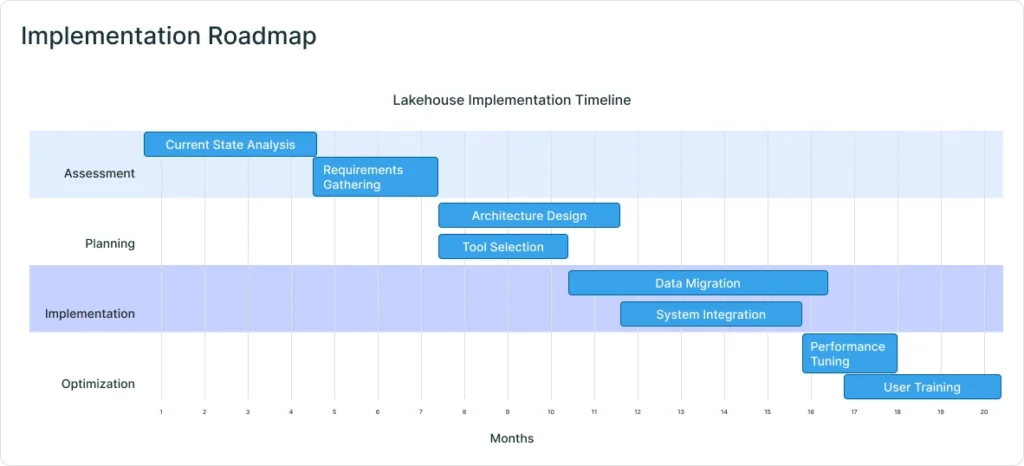
Implementation Roadmap
- Assessment: Audit current data landscape and identify integration points.
- Define Use Cases: Prioritize business goals—real-time inventory, customer 360, etc.
- Data Modeling & Governance: Establish unified schemas and governance policies.
- Data Migration: Gradually move data from legacy systems to the lakehouse.
- Integrate Analytics & ML: Connect BI tools and ML workflows to the unified platform.
- Iterate and Scale: Expand use cases, optimize performance, and ensure ongoing governance.
- Continuous Optimization: Monitor, scale, and refine the architecture as business needs evolve.
Conclusion: The Future of Retail Data is Unified
As retail continues to evolve, the ability to harness data effectively becomes increasingly critical. Lakehouse architecture provides the foundation needed to thrive in this new landscape, enabling retailers to be more agile, customer-centric, and data-driven than ever before.
Ready to transform your retail operations? The time to embrace lakehouse architecture is now. Your competitors already are.
Discover how a lakehouse architecture can revolutionize your retail business. Contact us to learn more about implementation strategies and success stories.




